8.6 KiB
Day 2
Back to the basics: and, or, not, if
Before we do anything more interesting we're going to have to cover our logical basics. In Python these are not, and, or, and if.
not
- Type
x = Trueand press enter. - Type
xand press enter to see that x is true. - Type
not xand press enter.notinverts the value ofx. So ifxis True,not xis False. - Type
not not xand press enter.not not xinvertsnot x. You can chainnotas many times as you want. - Let's imagine we're building a weather app and we want to know if it's raining. Type
is_raining = Trueand press enter. - Type
print(f"should I wear a raincoat? {is_raining}")and press enter. - Today it's not raining. We could create a variable called
is_not_rainingbut we could also justnot. Typeprint(f"should I wear a raincoat? {not is_raining}") - Type
not 'hello'and press enter. This might seem strange but Python interprets a string asTrue.not 'hello'will returnFalse. - Type
not ''and press enter. An empty string in Python is False.not ''returnsTrue.
and
- In your terminal type
x = Trueand press enter. - Type
xand press enter to see that x is True. - Type
y = Trueand press enter. - Type
yand press enter to see that y is True. - Type
y and xand press enter.yis true andxis true, soyandxis true. - We're building our weather app to be more useful. We want to tell people if it's rainy and windy. Type
rainy = Trueand press enter. - Type
windy = Trueand press enter. - Type
rainy and windyand press enter. We get True because it's rainy and windy. - Today it's not windy. Type
rainy and not windyand press enter. We get False because it isn't rainy and windy. - Tomorrow it won't be windy and it also won't be rainy. Type
not rainy and not windyand press enter. We get False because neither weather conditions are met.
or
- In your terminal type
x = Trueand press enter. - Type
xand press enter to see that x is True. - Type
y = Falseand press enter. - Type
yand press enter to see that y is False. - Type
y or xand press enter.xis True so asking if x or y is true will result inTrue. - Our weather app has millions of downloads. Our data suggests people don't like when it's cold or raining. Let's tell them when it's cold or raining.
- Type
cold = Trueand press enter. - Type
raining = Trueand press enter. - Type
cold or rainingand press enter. We getTrue, it is cold and it is raining. - Today it isn't cold but it is raining. Type
not cold or raining. We getTrue, it is still raining outside. - Tomorrow it won't be cold and it won't be raining. Type
not cold or not raining. We getFalsebecause neither of our disliked weather conditions are met.
if
-
In your terminal type
x = Trueand press enter. -
Type
xand press enter to see that x is True. -
Type
y = Falseand press enter. -
Type
yand press enter to see that y is False. -
Type
if x:and press enter. You'll see a.... Python is waiting for another input. -
Type ++tab++
print('x is true!')and press enter. You should see another.... -
Press enter again. 'x is true!' will print to the terminal.
-
Type
if y:and press enter. Now type ++tab++print('y is true!')and press enter twice. You won't see anything print. -
Type
if not y:and press enter. Now type ++tab++print('y is false!')and press enter twice. You'll see 'y is false!') printed. -
Now that our weather app is sentient let's give it some decision making capability.
-
Type
raining = Trueand press enter. -
Type
if raining:and press enter. -
Type ++tab++
print('You should wear a rain jacket')and press enter twice. Your weather app can now tell you to wear a jacket if it's raining outside. -
Type
exit()to exit
Building a Terrible Weather App
-
Create a new file called
weather_app.pyby clicking the "add file" icon in the top left of VSCode. -
We're going to create an app where the user has to guess the weather. We're going to need the python random module to generate random weather conditions. Add the following to the top of the page:
import randomThis tells python we intend to use the
randompackage -
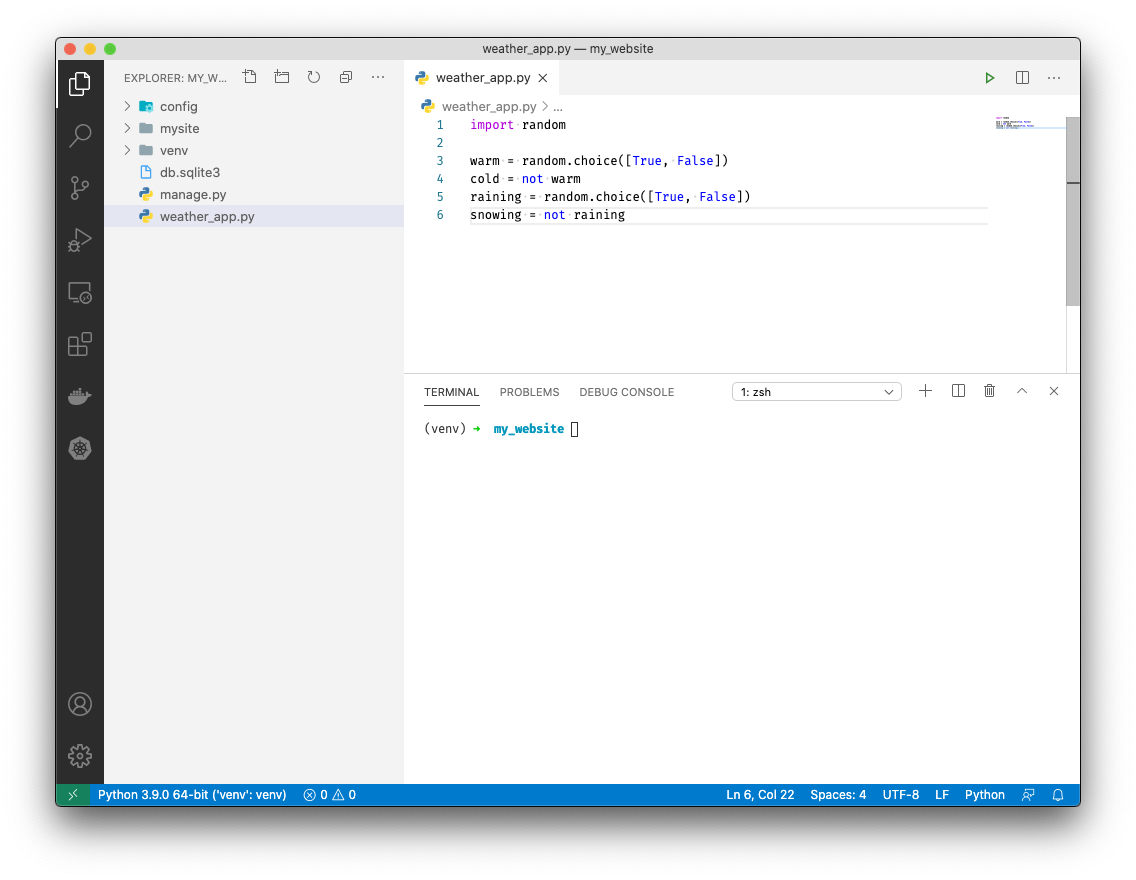
We'll generate 4 weather conditions. Add the following after
import randomwarm = random.choice([True, False]) cold = not warm raining = random.choice([True, False]) snowing = not rainingrandom.choice([True, False]) selects either True or False randomly.
-
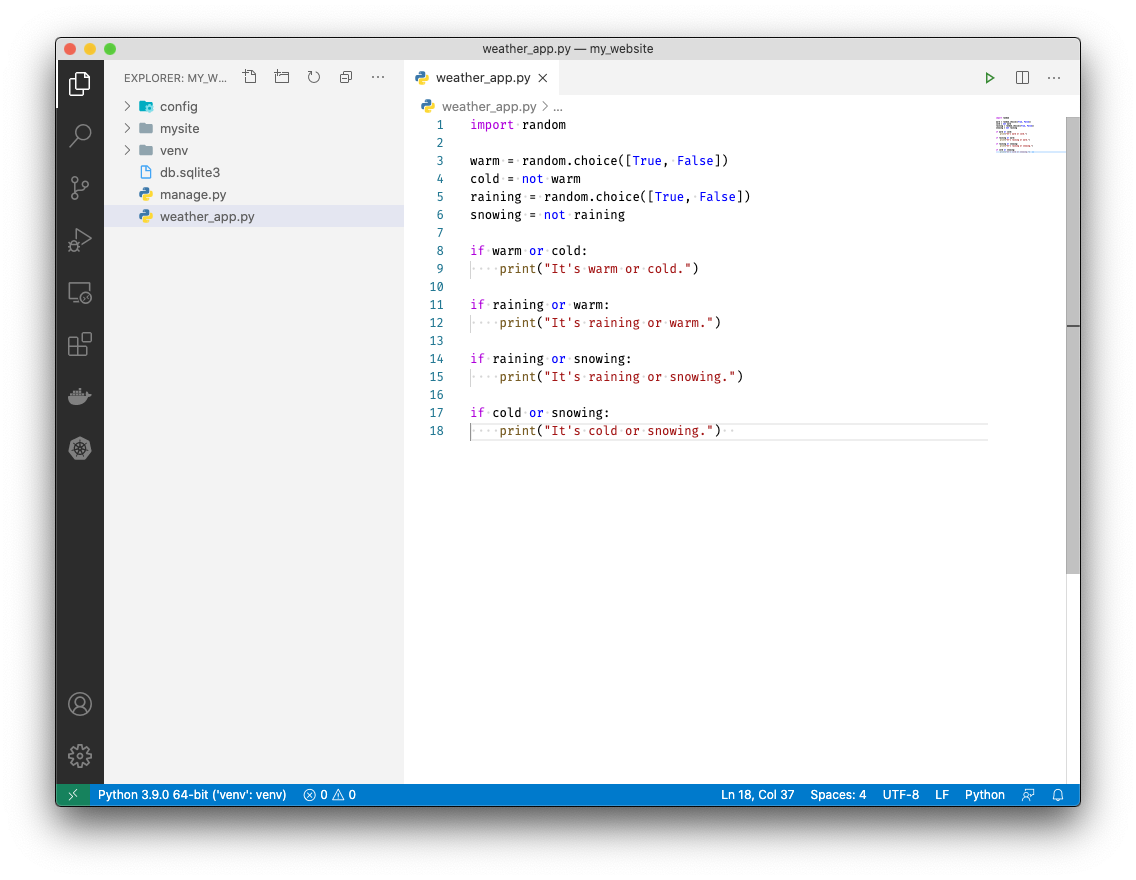
Let's print our weather conditions in a cryptic way. Add the following below our variables:
if warm or cold: print("It's warm or cold.") if raining or warm: print("It's raining or warm.") if raining or snowing: print("It's raining or snowing.") if cold or snowing: print("It's cold or snowing.")This will print weather conditions in pairs to make it more challenging for our users to guess the weather.
-
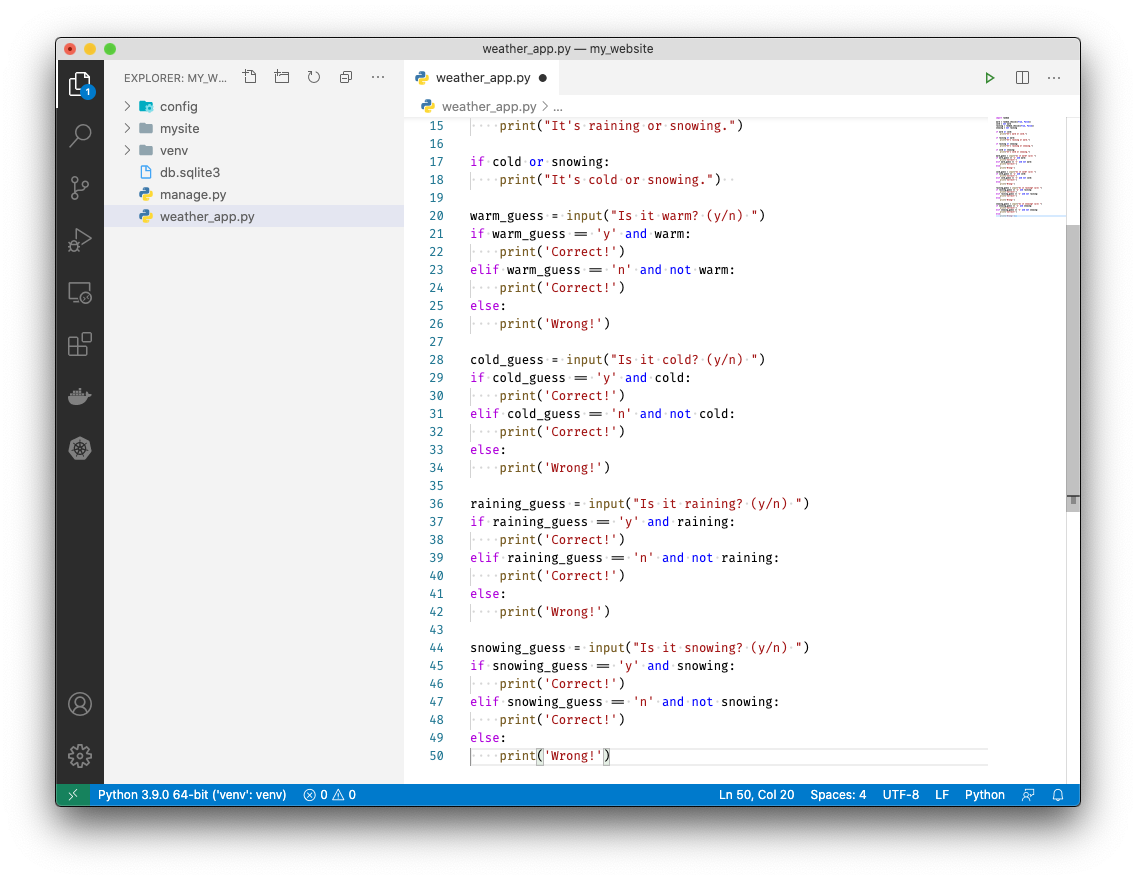
Now let's get our user input. Since we have 4 possible weather conditions we'll need 4 "guessing modules". Let's build the first one:
warm_guess = input("Is it warm? (y/n) ") if warm_guess == 'y' and warm: print('Correct!') elif warm_guess == 'n' and not warm: print('Correct!') else: print('Wrong!')We ask the user if it's warm. If they say 'y' and it is warm we tell them they got it right! If they guess wrong we tell them they are wrong.
-
We'll just repeat the guess module 3 more times for cold, raining, and snowing.
cold_guess = input("Is it cold? (y/n) ") if cold_guess == 'y' and cold: print('Correct!') elif cold_guess == 'n' and not cold: print('Correct!') else: print('Wrong!') raining_guess = input("Is it raining? (y/n) ") if raining_guess == 'y' and raining: print('Correct!') elif raining_guess == 'n' and not raining: print('Correct!') else: print('Wrong!') snowing_guess = input("Is it snowing? (y/n) ") if snowing_guess == 'y' and snowing: print('Correct!') elif snowing_guess == 'n' and not snowing: print('Correct!') else: print('Wrong!') -
Save with ++ctrl++ + S and run your weather app by typing
python weather_app.py. Try to guess the weather.
Pulling it all together with some Django
-
Let's make a weather app! Open "views.py" by clicking on it.
-
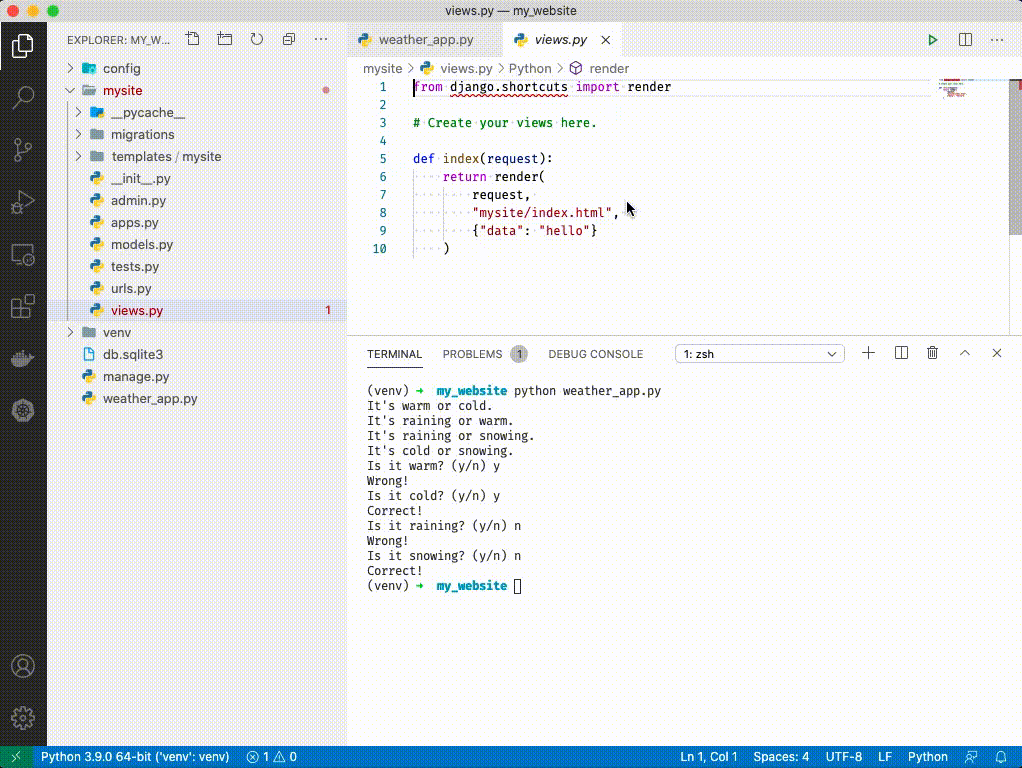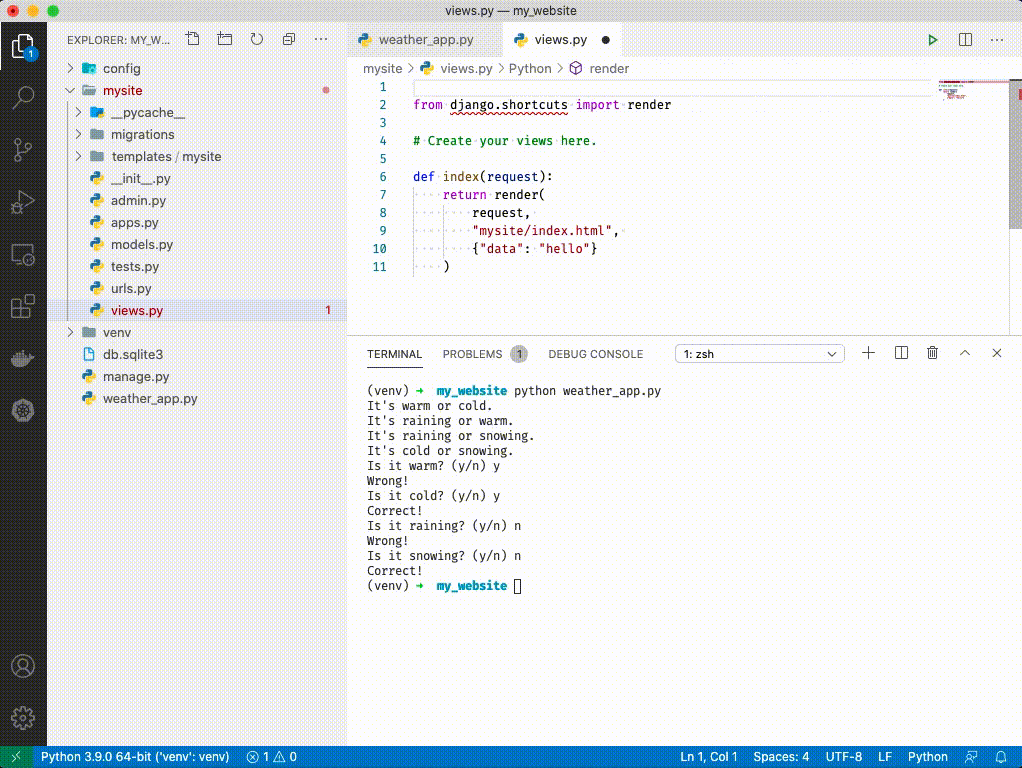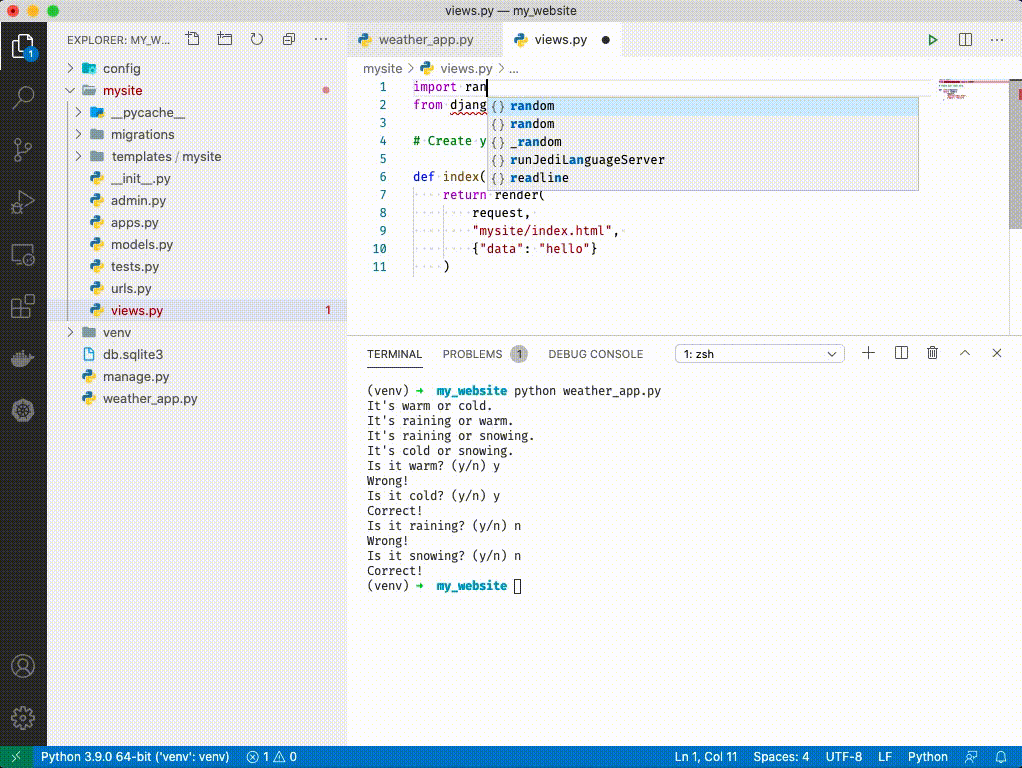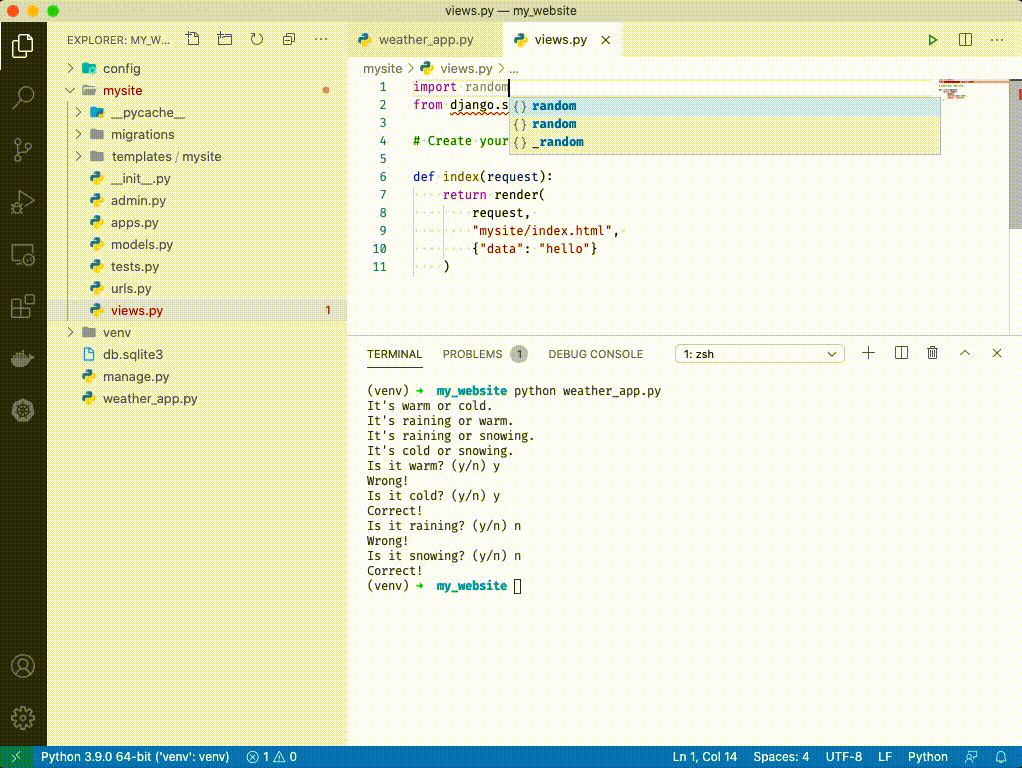
At the top of views.py add the following:
import random -
Now under all of our existing code in views.py add the following:
def weather(request): warm = random.choice([True, False]) cold = not warm raining = random.choice([True, False]) snowing = not raining if warm: temperature_report = "It's warm out! Don't wear a jacket." else: temperature_report = "It's cold out! Wear a jacket." if raining: precipitation_report = "It's raining! Bring an umbrella." else: precipitation_report = "It's snowing! Bring your skis." return render( request, "mysite/index.html", {"data": temperature_report + " " + precipitation_report} )This creates a new "view" in our django app.
-
Open mysite/urls.py by clicking on it.
-
Under
path('', views.index),add:path('weather/', views.weather), -
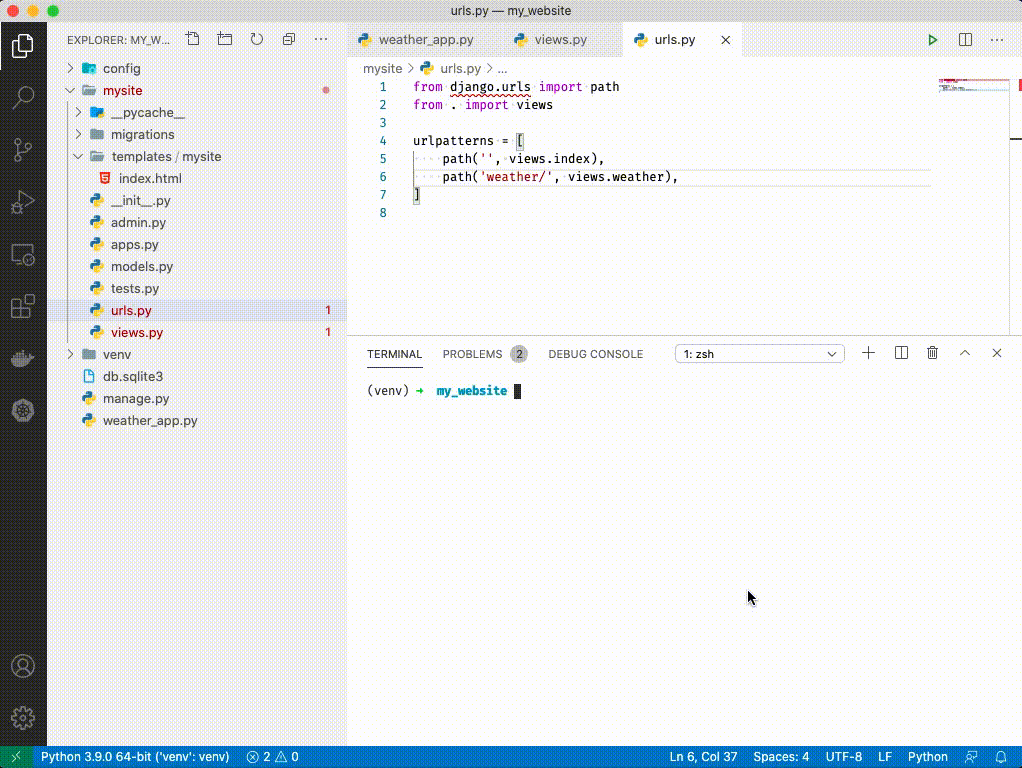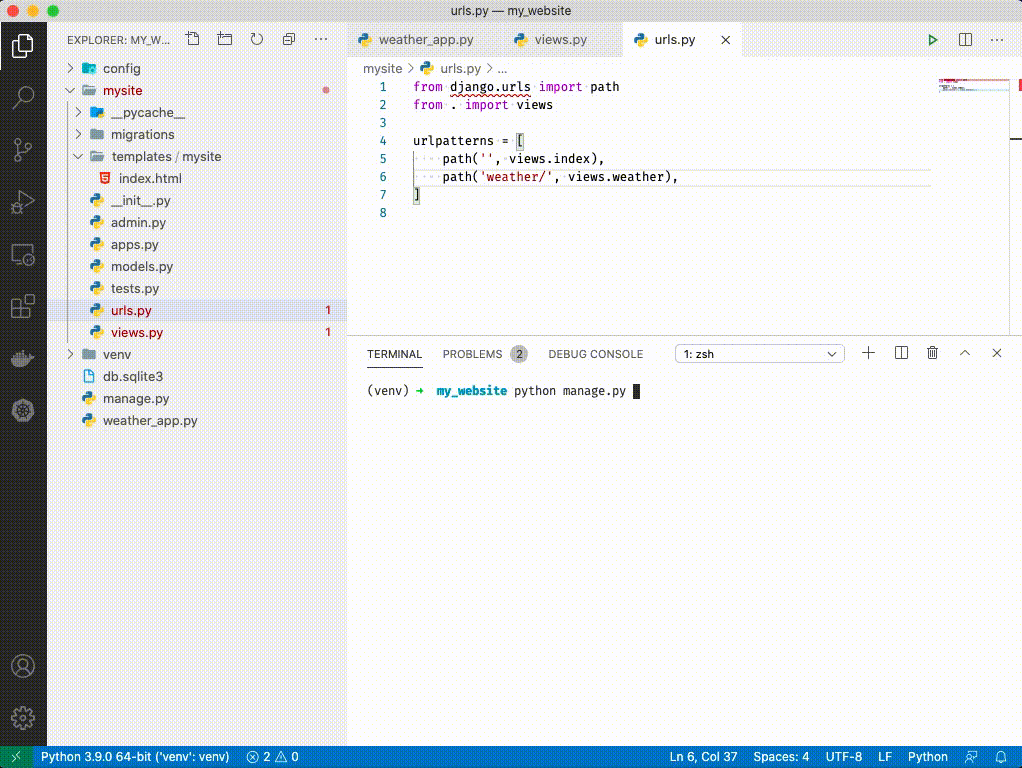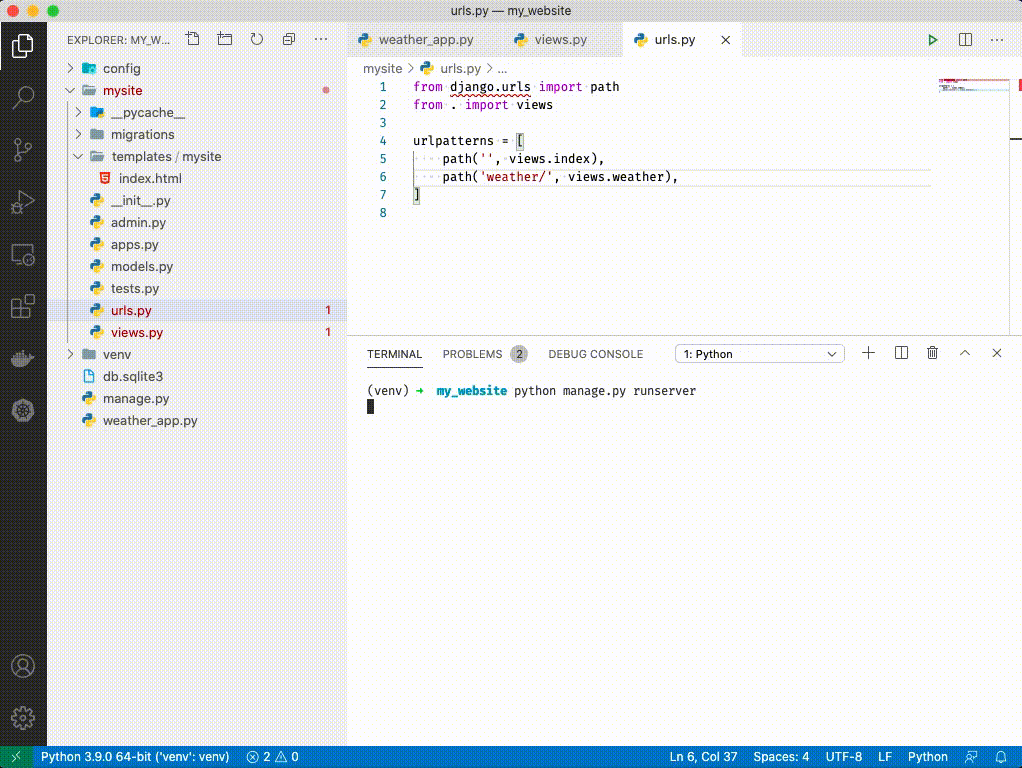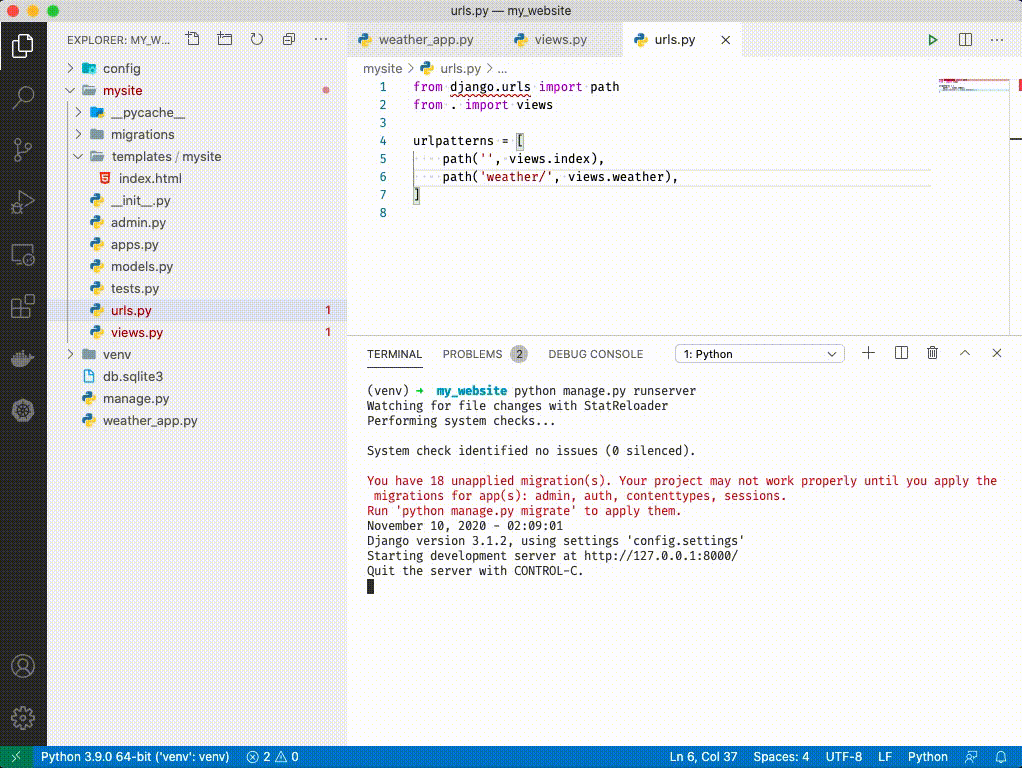
Run your server with
python manage.py runserver(if it isn't already running) -
Navigate to http://localhost:8000/weather
Congratulations! You've added a new page to your app!